Exploring Lagrangian Coherent Structures in the Atmosphere
.png)
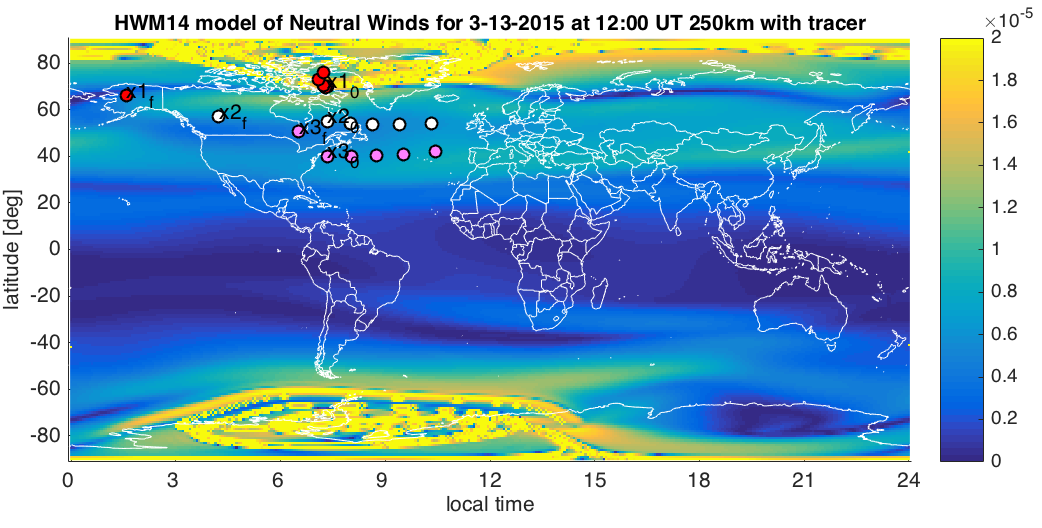
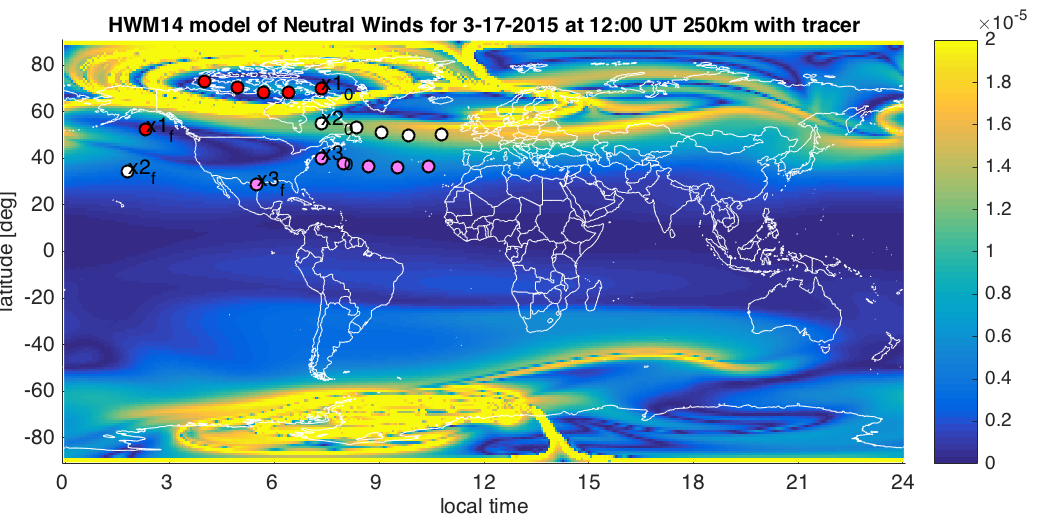
Lagrangian Coherent Structures (LCSs) are manifolds of maximum divergence or convergence in 2D or 3D time-varying flow fields. The study of LCSs has been used to predict material transport in numerous geophysical flows. In the arena of space science, coherent structures are most prominently visible in the form of aurorae. LCSs have been sought in models of the ionosphere and in stellar plasmas. To better understand possible interactions between coherent structuring in upper atmospheric plasmas with the neutral atmosphere, it is important to determine whether and how structuring appears in the atmosphere.
Support from National Science Foundation CAREER Award and Research Experience for Undergraduates
PI Seebany Datta-Barua
